자료구조 6. 연결 리스트
코드
- 모든 코드는 깃허브에서 확인하실 수 있습니다.
리스트(list)
- 순서가 있는 객체들의 모임
- 원하는 위치에 요소 추가(
insert) 및 삭제(delete) 가능
- 원하는 위치에 요소 추가(
- list의 기능
is_full: 리스트가 포화 상태인지 확인is_empty: 리스트가 비었는지 확인insert: 특정 위치에 요소를 추가delete: 특정 위치에 있는 요소를 제거clear: 모든 요소를 제거get_value: 특정 위치에 있는 값을 확인get_length: 리스트의 길이를 반환
- c언어
리스트 구조체 정의
1 2 3 4 5
typedef struct { int elements[MAX_LIST_SIZE]; int size; } List;
IsFull1 2 3 4
int IsFull(const List* list) { return list->size == MAX_LIST_SIZE; }
IsEmpty1 2 3 4
int IsEmpty(const List* list) { return list->size == 0; }
Insert1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
void Insert(List* list, int pos, int value) { assert(!IsFull(list)); assert(pos <= list->size); if (pos < 0) { pos = list->size; } for (int i = list->size; i > pos; --i) { list->elements[i] = list->elements[i - 1]; } list->elements[pos] = value; ++(list->size); }
Delete1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
void Delete(List* list, int pos) { if (pos < 0) { pos = list->size - 1; } if (pos >= list->size || pos < 0) { return; } for (int i = pos; i < list->size - 1; ++i) { list->elements[i] = list->elements[i + 1]; } --(list->size); }
- 앞으로 당길 때, 마지막 쓰레기 값을 제거하지 않았음
size를 감소시켰기 때문에 제거하지 않아도 상관 없음
Clear1 2 3 4
void Clear(List* list) { list->size = 0; }
- 값을 제거하는 대신
size를0으로 설정
- 값을 제거하는 대신
GetValue1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
int GetValue(const List* list, int pos) { if (pos < 0) { pos = list->size - 1; } assert(pos >= 0 && pos < list->size); return list->elements[pos]; }
GetLength1 2 3 4
int GetLength(const List* list) { return list->size; }
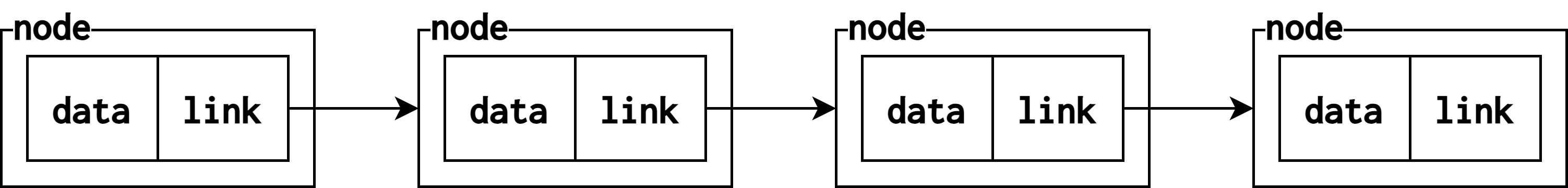
연결 리스트(linked list)
- 노드(node): 연결 리스트의 기본 단위
- 데이터 필드(data field): 실질적인 값을 저장
- 링크 필드(link field): 다음 노드의 주소를 저장
- 연결 리스트의 기능
is_empty: 연결 리스트가 비었는지 확인get_node: 특정 위치에 있는 노드를 확인insert: 특정 위치에 요소를 추가delete: 특정 위치에 있는 요소를 제거clear: 모든 요소를 제거get_length: 연결 리스트의 길이를 반환reverse: 연결 리스트의 순서를 반전
- 연결 리스트의 장단점
- 장점
- 삽입, 삭제가 용이
- 연속된 메모리 공간이 필요 없음
- 메모리 공간만 충분하다면 크기 제한이 없음(유동적인 크기)
- 단점
- 구현이 어려움
- 메모리 파편화
- 장점
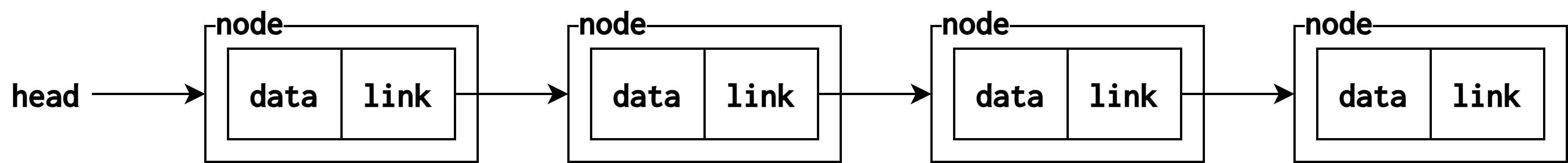
단순 연결 리스트(singly linked list)
- 하나의 링크 필드를 이용해 연결
head가 첫 노드를 가리킴- 마지막 노드의 링크는
NULL - c언어
노드&단순 연결 리스트 구조체 정의
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node* link; } Node; typedef struct { Node* head; int length; } SinglyLinkedList;
IsEmpty1 2 3 4
int IsEmpty(const SinglyLinkedList* list) { return list->head == NULL; }
GetNode1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Node* GetNode(const SinglyLinkedList* list, const int pos) { if (pos < 0 || pos >= list->length) { return NULL; } Node* search = list->head; for (int i = 0; i < pos; ++i) { search = search->link; } return search; }
Insert1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
int Insert(SinglyLinkedList* list, const int pos, const int data) { Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if (newNode == NULL) { return 0; } newNode->data = data; if (pos == 0) { newNode->link = list->head; list->head = newNode; ++(list->length); return 1; } Node* prev; if ((prev = GetNode(list, pos - 1)) == NULL) // if pos is wrong { free(newNode); return 0; } newNode->link = prev->link; prev->link = newNode; ++(list->length); return 1; }
Delete1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
void Delete(SinglyLinkedList* list, const int pos) { if (pos == 0) { Node* current = list->head; list->head = current->link; free(current); --(list->length); return; } Node* prev = GetNode(list, pos - 1); if (prev == NULL || prev->link == NULL) // if pos is wrong { return; } Node* current = prev->link; prev->link = current->link; free(current); --(list->length); }
Clear1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
void Clear(SinglyLinkedList* list) { Node* search = list->head; Node* temp; while (search != NULL) { temp = search->link; free(search); search = temp; } list->head = NULL; list->length = 0; }
GetLength1 2 3 4
int GetLength(const SinglyLinkedList* list) { return list->length; }
Reverse1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
void Reverse(SinglyLinkedList* list) { Node* current = list->head; Node* prev = NULL; Node* next; while (current != NULL) { next = current->link; current->link = prev; prev = current; current = next; } list->head = prev; }
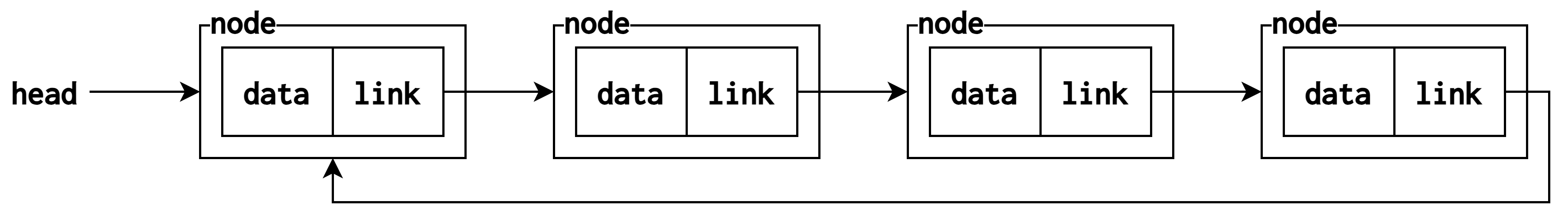
원형 연결 리스트(circular linked list)
- 마지막 노드의 링크가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키는 연결 리스트
- 장점
- 한 노드에서 모든 노드로의 접근이 가능
head가 마지막 노드를 가리키도록 설정하면 처음과 마지막에 노드를 삽입하기 편함
- c언어
노드&단순 연결 리스트 구조체 정의
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node* link; } Node; typedef struct { Node* head; int length; } CircularLinkedList;
IsEmpty1 2 3 4
int IsEmpty(const CircularLinkedList* list) { return list->head == NULL; }
GetNode1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Node* GetNode(const CircularLinkedList* list, const int pos) { if (pos < 0 || pos >= list->length || IsEmpty(list)) { return NULL; } Node* search = list->head->link; for (int i = 0; i < pos; ++i) { search = search->link; } return search; }
Insert1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41
int Insert(CircularLinkedList* list, const int pos, const int data) { Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if (newNode == NULL) { return 0; } newNode->data = data; Node* prev = GetNode(list, pos - 1); if (pos == 0) { if (IsEmpty(list)) { newNode->link = newNode; list->head = newNode; ++(list->length); return 1; } prev = list->head; } else if (pos == list->length) { list->head = newNode; } if (prev == NULL) { free(newNode); return 0; } newNode->link = prev->link; prev->link = newNode; ++(list->length); return 1; }
Delete1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
void Delete(CircularLinkedList* list, const int pos) { Node* prev = GetNode(list, pos - 1); if (pos == 0) { if (list->length == 1) { free(list->head); list->head = NULL; --(list->length); return; } prev = list->head; } else if (pos == list->length - 1) { list->head = prev; } if (prev == NULL || prev->link == NULL) { return; } Node* current = prev->link; prev->link = current->link; free(current); --(list->length); }
Clear1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
void Clear(CircularLinkedList* list) { if (IsEmpty(list)) { return; } Node* search = list->head; Node* temp; do { temp = search->link; free(search); search = temp; } while (search != list->head); list->head = NULL; list->length = 0; }
GetLength1 2 3 4
int GetLength(const CircularLinkedList* list) { return list->length; }
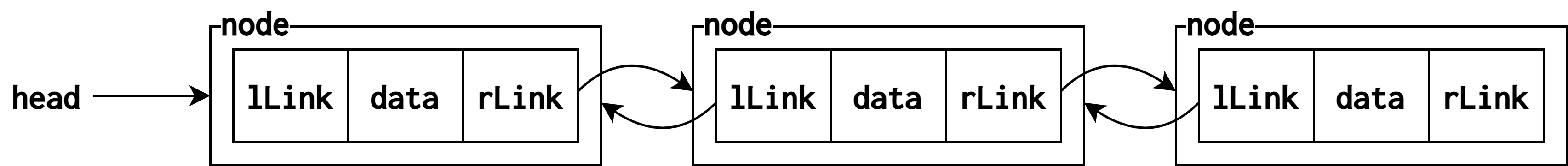
이중 연결 리스트(doubly linked list)
- 하나의 노드가 선행 노드와 후속 노드에 대한 두개의 링크를 가지는 연결 리스트
- 장단점
- 장점
- 선행 노드를 쉽게 알 수 있음
- 단점
- 공간을 많이 차지
- 장점
- c언어
노드&단순 연결 리스트 구조체 정의
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node* lLink; struct Node* rLink; } Node; typedef struct { Node* head; int length; } DoublyLinkedList;
IsEmpty1 2 3 4
int IsEmpty(const DoublyLinkedList* list) { return list->head == NULL; }
GetNode1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
Node* GetNode(const DoublyLinkedList* list, const int pos) { if (pos < 0 || pos >= list->length || IsEmpty(list)) { return NULL; } Node* search = list->head; for (int i = 0; i < pos; ++i) { search = search->rLink; } return search; }
Insert1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
int Insert(DoublyLinkedList* list, const int pos, const int data) { Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if (newNode == NULL) { return 0; } newNode->data = data; if (pos == 0) { newNode->rLink = list->head; if (list->head != NULL) { list->head->lLink = newNode; } list->head = newNode; ++(list->length); return 1; } Node* prev; if ((prev = GetNode(list, pos - 1)) == NULL) { free(newNode); return 0; } if (prev->rLink != NULL) { prev->rLink->lLink = newNode; } newNode->rLink = prev->rLink; newNode->lLink = prev; prev->rLink = newNode; ++(list->length); return 1; }
Delete1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
void Delete(DoublyLinkedList* list, const int pos) { if (pos == 0) { Node* current = list->head; list->head = current->rLink; if (list->head != NULL) { list->head->lLink = NULL; } free(current); --(list->length); return; } Node* prev = GetNode(list, pos - 1); if (prev == NULL || prev->rLink == NULL) { return; } Node* current = prev->rLink; prev->rLink = current->rLink; current->rLink->lLink = prev; free(current); --(list->length); }
Clear1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
void Clear(DoublyLinkedList* list) { Node* search = list->head; Node* temp; while (search != NULL) { temp = search->rLink; free(search); search = temp; } list->head = NULL; list->length = 0; }
GetLength1 2 3 4
int GetLength(const DoublyLinkedList* list) { return list->length; }
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.